Source:
Bank Industry Overview: Indonesia
Primary Credit Analyst:
Adrian Chee, Singapore
Publication date: 17-Jan-06, 21:31:31 EST
The outlook on the Indonesian banking sector remains stable. The sector has slowly begun to rebuild its financial base since the 1997 economic crisis, and progress has accelerated in the past three years. The level of capitalization in the banking system has risen due to improving investor confidence following several completed privatization programs. The industry risk profile, nevertheless, remains high by international standards because of the high-risk operating environment, characterized by slow corporate debt restructuring, volatile exchange rates, and the need for reforms in the legal system. These factors are partially mitigated by improved political stability, a relatively more stable credit quality and earnings performance, and strengthening capitalization levels. Going forward, the Indonesian banks are expected to experience increasing pressure on their interest margins, from higher deposit costs, as well as in their quality of loan portfolio, in the current rising interest rate environment.
Positive factors
Infusion of best practices and expertise in management strategies, risk management practices, human resources, and IT systems, as a result of foreign institutional investment in major private commercial banks in Indonesia.
Structural improvement where consolidation has reduced the number of banks to around 130 in July 2005, from 208 in 1998. In addition, banks have sought to improve their operating efficiency.
Improved capitalization. The government's large-scale recapitalization program has improved the capital position of banks, which have also benefited from recovering profitability in the past few years. Nevertheless, the banks' capitalization might face renewed pressure as they restart lending to productive sectors of the economy and seek to bolster the level of provisioning for nonperforming assets (NPAs).
Improving asset quality. The banking system's regulatory gross nonperforming loan (NPL) ratio has steadily improved to 8.5% in July 2005, from 32.8% in December 1999. The trend for NPAs, which include NPLs, foreclosed properties, and some restructured loans, is estimated to improve to 15% of total loans in December 2005, from about 50% in 1999.
Negative factors
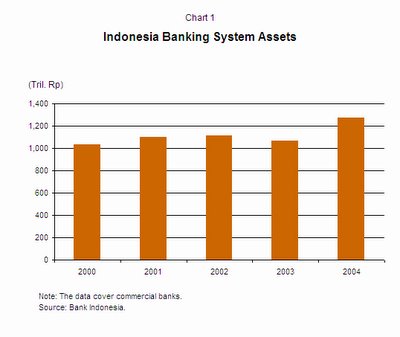
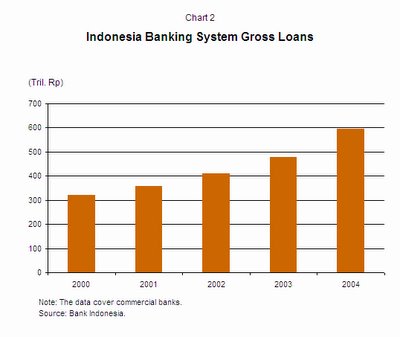
The resumption of banks' role as financial intermediaries. While the system's loan growth has been strong over the past two years, the loan to asset ratio is still relatively low, at around 40% in 2004. This was partly attributed to the lack of productive loan opportunities in the real sector, and also reflected the corporate sector's high business risks and the large amount of NPLs due for restructuring. The ratio is expected to increase as banks have continued to post strong growth in their lending portfolios in 2005.
Susceptibility of credit quality in a higher interest-rate environment. While the system has demonstrated an overall improvement after the Asian financial crisis, the sharp growth in loans in the past two to three years could strain loan quality following a time lag for NPLs, particularly as interest costs rise as a result of the rising interest rate environment.



No comments:
Post a Comment